School Site Council
The Role of a SSC
What is a School Site Council?
SSC’s make decisions at the school site regarding site programs and categorical programs, in addition to spending. SSC's are made up of parents, community members, and school personnel. The SSC decides upon academic instructional programs and all related categorical resource expenditures for a school.
A SSC is a school-community representative body made up of:
- Principal
- Teachers
- Other School Personnel
- Parents or Community
Education Code Section 52852 (formerly 52012) specifies that a school improvement plan shall be developed by a school site council (SSC). The law says, “The SSC shall be composed of the principal; representatives of teachers selected by teachers at the school; other school personnel selected by peers at the school; parents of pupils attending the school selected by such parents; and, in secondary schools, pupils selected by pupils attending the school.”
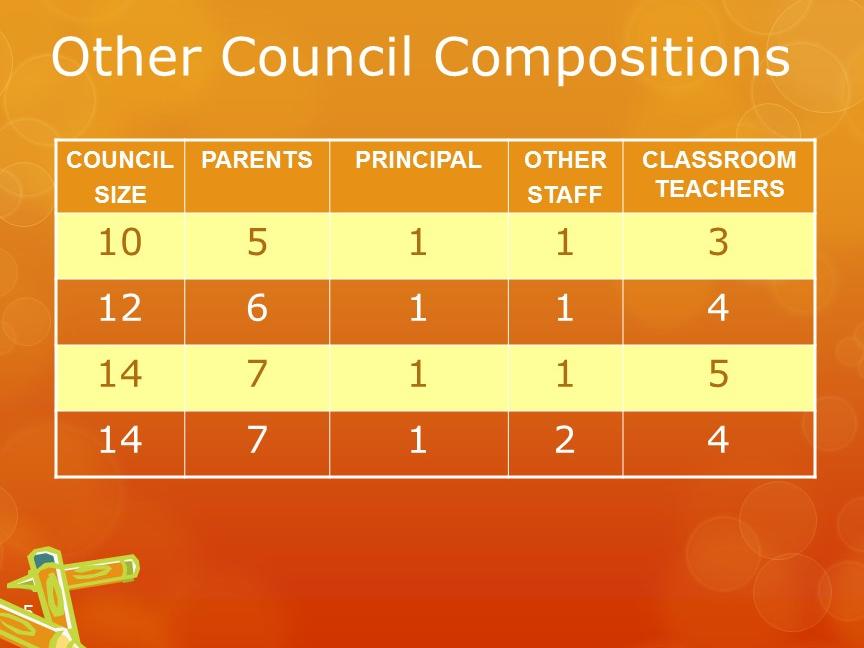
Middle grades SSC composition falls under the rules for secondary schools. For the first time students are included in the SSC.
At the secondary level the council shall be constituted to ensure parity between the principal, classroom teachers and other school personnel; (b) equal numbers of parents or other community members selected by parents, and pupils. At both the elementary and secondary levels, classroom teachers shall comprise the majority of persons represented under category (a). (Education Code Section 52852). Education Code Section 52852 states that parents or community members on the SSC may not be employed by the school district.
Continued School Improvement:
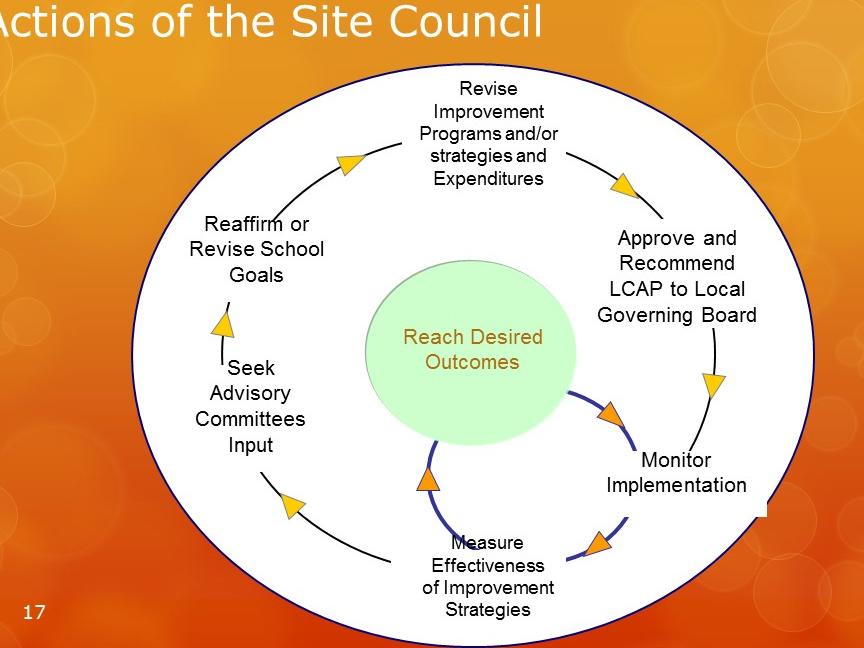
School Improvement is a program for elementary, intermediate, and secondary schools to continue improvement of instruction, services, school environment, and organization at school sites according to plans developed by School Site Councils. The California Education Code states the school site council should:
- Measure effectiveness of improvement strategies at the school.
- Seek input from school advisory committees.
- Reaffirm or revise school goals.
- Revise improvement strategies and expenditures.
- Recommend the approved single plan for student achievement (SPSA) to the governing board.
- Monitor implementation of the SPSA
Single Plan for Student Achievement Plan
The purpose of the Single Plan for Student Achievement (SPSA) is to raise the academic performance of all students to the level of state achievement standards. California Education Code sections 41507, 41572, and 64001 and the federal No Child Left Behind Act (NCLB) require each school to consolidate all school plans related to state and federal funding. The California Department of Education has developed a planning guide and template for local educational agencies (LEAs) to meet the program requirements. JMS SPSA Plan for 2016-2017

JMS SSC Meetings 2016-2017
3:15pm on Tuesday in the School Library
September 20, 2016
October 25, 2016
January 17, 2017
February 21, 2017
April 25, 2017
JMS SSC Meeting Agendas and Meeting Minutes 2016-2017
3:15pm on Tuesday in the School Library
September 20, 2016 Agenda and Minutes
October 25, 2016 Agenda and Minutes
January 17, 2017 Agenda and Minutes
February 21, 2017 Agenda and Minutes
April 25, 2017 Agenda and Minutes
Local Control and Accountability Plan
What is the Local Control and Accountability Plan?
The LCAP is a critical part of the new Local Control Funding Formula (LCFF). Each school district must engage parents, educators, employees and the community to establish these plans. The plans will describe the school district’s overall vision for students, annual goals and specific actions the district will take to achieve the vision and goals. The LCAPs must focus on eight areas identified as state priorities. The plans will also demonstrate how the district’s budget will help achieve the goals, and assess each year how well the strategies in the plan were able to improve outcomes. JMS LCAP 2014-2017
What are the 8 State priority areas that must be addressed?
There are eight areas for which school districts, with parent and community input, must establish goals and actions. This must be done both district-wide and for each school. The areas are:
- Providing all students access to fully credentialed teachers, instructional materials that align with state standards, and safe facilities.
- Implementation of California’s academic standards, including the Common Core State Standards in English language arts and math, Next Generation Science Standards, English language development, history social science, visual and performing arts, health education and physical education standards.
- Parent involvement and participation, so the local community is engaged in the decision-making process and the educational programs of students.
- Improving student achievement and outcomes along multiple measures, including test scores, English proficiency and college and career preparedness.
- Supporting student engagement, including whether students attend school or are chronically absent.
- Highlighting school climate and connectedness through a variety of factors, such as suspension and expulsion rates and other locally identified means.
- Ensuring all students have access to classes that prepare them for college and careers, regardless of what school they attend or where they live.
- Measuring other important student outcomes related to required areas of study, including physical education and the arts.
In addition to these eight areas, a district may also identify and incorporate in its plan goals related to its own local priorities.